The introduction of the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) is fundamentally changing sustainability reporting for companies in Europe. In this guide, you will learn everything you need to know about the new EU directive, what exactly it entails and what deadlines and challenges companies will face.
What exactly is CSRD?
The CSRD (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive) is an EU directive that extends the previous Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD). The aim of the CSRD is to standardize and improve reporting on sustainability-related topics. Companies are to publish more detailed information on their social and environmental impact in order to promote transparency and accountability. This directive requires companies to comply with comprehensive sustainability standards and integrate them into their reports.
What is the difference between CSRD and ESG?
While ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) is a methodology for assessing a company’s sustainability performance, the CSRD provides the regulatory basis for reporting. ESG is a framework that investors and other stakeholders use to assess the sustainability practices of companies. The CSRD, on the other hand, defines what specific information on ESG issues must be reported and how these reports should be structured. Topics such as corporate governance and the consideration of stakeholder interests are explicitly regulated in the CSRD in order to create a comprehensive reporting framework.
How ESRS defines CSRD reporting requirements
The CSRD is based on the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS), which establish a mandatory framework for reporting on sustainability aspects. The ESRS define detailed requirements and standardized formats for reporting to ensure consistent and comparable disclosure of ESG data across the EU. They include specific guidelines on topics such as climate protection, human rights, circular economy, and biodiversity. Companies must demonstrate how their business activities align with the goals of the EU Taxonomy and the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The ESRS approach ensures that reports not only meet regulatory requirements but also provide valuable insights for stakeholders.

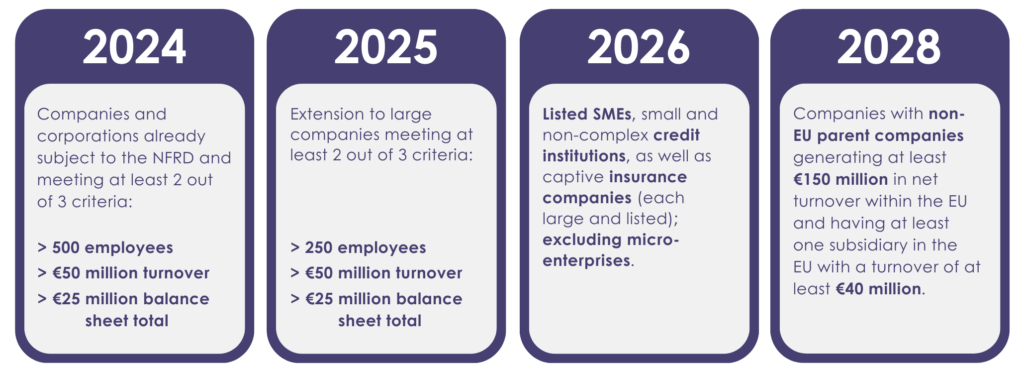
The roadmap to compliance with CSRD obligations
The CSRD reporting will be introduced gradually, with obligations being extended from year to year. Here is the detailed timetable:
2024: Obligation for NFRD companies
Starting from the 2024 financial year, companies that are already subject to the NFRD must prepare their sustainability reports in accordance with the new CSRD reporting requirements. This primarily affects large capital market-oriented companies with more than 500 employees. The reports must be integrated into the annual financial statements and prepared in accordance with ESRS standards. In addition, companies are obliged to include climate risks in their reports in order to clarify the potential impact on their business strategies.
2025: New reporting obligations for medium-sized companies
From 2025, the CSRD will be extended to all large companies that meet two of the following three criteria: more than 250 employees, a turnover of more than 50 million euros or a balance sheet total of more than 25 million euros. This extension of the reporting obligations requires early preparations to adapt the processes for data collection and financial reporting.
2026: Focus on small and medium-sized enterprises (SME)
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SME) that are listed on the stock exchange, non-complex financial institutions and specialized insurance companies must submit their first reports in accordance with the CSRD reporting obligation from 2026. Simplified standards will apply to these companies until 2028 to facilitate the transition. The inclusion of specific sustainability targets will play a central role in their corporate reporting.
2028: International requirements and transition periods
In 2028, large international companies that have a branch in the EU and generate a turnover of more than 150 million euros in the EU will also be affected. These companies must fulfill the requirements of the CSRD and publish corresponding reports. An overview of the entire supply chain, including the EU taxonomy and the analysis of climate risks, is necessary here.
The role of digitalization in compliance with the CSRD
Digitalization plays a central role in fulfilling the CSRD. The use of automated reporting and analysis tools such as Intito ESG enables companies to collect and process data efficiently. They not only help with compliance with regulatory requirements, but also offer advantages in the visualization and communication of results to stakeholders. Companies that rely on reporting tools can better monitor their reporting obligations, improve their sustainability strategy and increase transparency for all stakeholders.
Challenges in implementing CSRD
The implementation of the CSRD poses various challenges. One of the biggest hurdles is the collection and processing of extensive and heterogeneous data. Companies must ensure that their data systems meet the requirements of the sustainability standards and enable auditable reports. Furthermore, the integration of ESG factors into existing reporting processes represents an additional complexity that requires both technical expertise and close collaboration between different departments. The pressure to meet deadlines and the need to ensure a high level of transparency can be a burden for companies without sufficient preparation.
Practical tips for preparing for CSRD reporting
Companies should start preparing for the requirements of the CSRD as early as possible. A first step is to carry out a comprehensive inventory of current sustainability strategies and reports. It is advisable to put together a team from different departments to take care of data collection and reporting. Implementing specialized software solutions for data collection and analysis can also be crucial to reduce effort and improve accuracy. Structured employee training on sustainability standards and CSRD requirements provides a solid foundation for successful implementation.

Conclusion: Opportunities and challenges of the new reporting obligations
The introduction of the CSRD represents a significant challenge, but also offers opportunities for companies. Adapting to the new reporting standards can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. At the same time, it leads to greater transparency and improves market positioning. Companies that implement the necessary systems and processes at an early stage will benefit from a significant competitive advantage. We support you and your company with ESG reporting in order to successfully master your challenges and make sustainable progress.








